Market Insight: Guest Articles
Common Data Center Acronyms
by Ned Fennie, Jr.
Co founder FENNIE+MEHL Architects
April 2007
A few terms used by I.T. professionals and their definitions:
- 24-7 or 24-365
- This is the common way to describe systems which are always on, e.g. 24 hours a day for seven days a week. 24-365 refers to systems that run all year, meaning no downtime…ever.
- 25 Pair, 300 Pair, et al
- A common copper telephone (and data) cable. The actual cable bundles or wraps together 25 discrete pairs of solid copper wires. (See twisted pair)
- ASHRAE
- The American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers advances the arts and sciences of heating, ventilation, air conditioning and refrigeration. They write a lot of the standards for data center systems designs.
- ATS
- Automatic Transfer Switch; this is a switch which instantly transitions the electrical power for a system from line power (from the utility company) to power from an emergency generator and is considered an integral part of a generator-type UPS system.
- Backbone
- A high-speed connection that links many networks, many times this is accomplished utilizing a fiber optic cable.
- Bandwidth
- The range of transmission frequencies that a network can use. The greater the bandwidth, the greater the amount of information than can travel on the network at one time.
- Blade Server
 Thin horizontally (or vertically) mounted computer server that can be stacked in a rack.
Thin horizontally (or vertically) mounted computer server that can be stacked in a rack.- BTU or BTUH
- British Thermal Units or British Thermal Units per Hour. The measure of heat produced by a HVAC system. To put in perspective 1 “ton of cooling,“ a common unit in refrigeration and air conditioning applications, is 12,000 BTU/h. It is the amount of power needed to melt one ton of ice in 24 hours
- CAT3
- Category 3 cable, commonly known as Cat 3, is an unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cable designed to reliably carry data up to 10 Mbit/s, with a possible bandwidth of 16 MHz. It is part of a family of copper cabling standards defined jointly by the Electronic Industries Alliance and the Telecommunications Industry Association. Category 3 was a popular cabling format among computer network administrators in the early 1990s, but fell out of popularity in favor of the very similar, but higher performing, Cat 5 standard. Presently, most new structured cable installations are built with Cat 5e or Cat 6 cable. Cat 3 is currently still in use in two-line telephone systems, although Cat 5 or higher could do the same work while facilitating a transition to VOIP.
- CAT5e
- Category 5 cable, commonly known as Cat 5, is a twisted pair cable type designed for high signal integrity. Usually it is unshielded but shielded cables can also be purchased. Category 5 has been superseded by the Category 5e or “Enhanced” specification. This type of cable is often used in structured cabling for computer networks such as Ethernet, although it is also used to carry many other signals such as basic voice services, token ring, and ATM (at up to 155 Mbit/s, over short distances).
- CAT6
- Cat 6- Category—6, (ANSI/TIA/EIA-568-B.2-1) is a cable standard for Gigabit Ethernet and other network protocols that is backward compatible with the Category 5/5e and Category 3 cable standards. Cat-6 features more stringent specifications for crosstalk and system noise. The cable standard is suitable for 10BASE-T / 100BASE-TX and 1000BASE-T (Gigabit Ethernet) connections. It provides performance of up to 250 MHz.
- “Copper”
- Telephone (or data) cable made up of solid copper (see Twisted Pair)
- CPU
- Central Processing Unit. The main processing chip in a computer system.
- CRAC
- Computer Room Air Conditioner
- CRT
- Cathode Ray Tube. Usually refers to a CRT display or an old style TV-type monitor. These are quickly being replaced with LCD’s.
- Dark Fiber
- Bulk, raw fiber. Dark fiber is optical fiber that spans some geographic area and is sold to carriers and large businesses without any optical or electronic signaling in its path. The customer is responsible for adding the transmission system at both ends.
- DNS
- (Domain Name Server). A computer on the Internet, which translates between a domain name (e.g., www.oxy.edu) and a numeric Internet address (134.69.5.3)
- EPO
- Emergency Power Off; usually adjective for switch. This switch is required for all data rooms of a certain size. It allows firefighting personnel to kill all power to the room from one central location.
- Ethernet
- Ethernet is a large, diverse family of frame-based computer networking technologies that operates at many speeds for local area networks (LANs). Ethernet has been standardized as IEEE 802.3. The combination of the twisted pair versions of ethernet for connecting end systems to the network with the fiber optic versions for site backbones become the most widespread wired LAN technology in use from the 1990s to the present.
- Extranet
- A private network that is used to share part of a business’s information or operations with suppliers, vendors, partners, customers, or other businesses. An extranet can be viewed as part of a company’s intranet that is extended to users outside the company.
- Fault Tolerant
- Fault-tolerant design refers to a method for designing a system so it will continue to operate, possibly at a reduced level (also known as “graceful degradation”), rather than failing completely, when some part of the system fails. The term is most commonly used to describe computer-based systems designed to continue more or less fully operational with, perhaps, a reduction in throughput or an increase in response time in the event of some partial failure. That is, the system as a whole is not stopped due to problems either in the hardware or the software. An example in another field is a motor vehicle designed so it will continue to be drivable if one of the tires is punctured.
- “Fiber”
- A common descriptor for Fiber Optic Cable. This cable is made up of many thin strands of glass fibers where signals are sent via pulses of light instead of electrical current.
- Form Factor
- The 3d size of a device, or shape. (E.g. different manufacturers who make PC’s to accommodate the same class Motherboard are said to conform to the same form factor.)
- Footprint
- The actual floor size of a device or piece of equipment.
- FTP
- File Transfer Protocol. The tool you would use to transfer files through the Internet from one computer to another. For example, you would use an FTP to upload your web page from where you built it (like your computer at home) to a web site so that all of your friends and neighbors can look at it.
- Gateway
- A computer that links two networks, routing IP data and often converting protocols or messages from one network to the other. The term can also refer to a system capability that provides direct access to other remote networks or services.
- HTML
- Hyper Text Markup Language. The language/code used to create web pages. HTML is not really a programming language, but a way to format text by placing marks around the text. For example HTML allows you to make a word bold or underline it. HTML is the foundation for most web pages.
- Intranet
- (compare Internet and Extranet). Internal systems, based on Internet technology, designed to connect the members of a specific group or single company (a closed-user group). An Intranet is nothing more than a private Internet. In other words, it is a private network, usually a LAN or WAN, that enables the use of Internet-based applications in a secure and private environment. As on the public Internet, Intranets can host Web servers, FTP servers, and any other IP-based services.
- ISO 9000
- ISO 9000 is a family of standards for quality management systems. ISO 9000 is maintained by ISO, the International Organization for Standardization and is administered by accreditation and certification bodies. For a manufacturer, some of the requirements in ISO 9001 (which is one of the standards in the ISO 9000 family) would include:
- a set of procedures that cover all key processes in the business;
- monitoring manufacturing processes to ensure they are producing quality product;
- keeping proper records;
- checking outgoing product for defects, with appropriate corrective action where necessary; and
- regularly reviewing individual processes and the quality system itself for effectiveness.
- IT
- Information Technology. It used to be called (a long time ago…) MIS, Management Information Systems, but management aren’t the only ones who use these systems any more, so it is now just called generically IT.
- KA or KW (Power factor)
- The power factor of an AC electric power system is defined as the ratio of the real power (KW or Kilowatts) to the apparent power (KA or Kilovolt Amps), and is a number between 0 to 1 inclusive. Real power is the capacity of the circuit for performing work in a particular time. Apparent power is the product of the current and voltage of the circuit. Due to energy stored in the load and returned to the source, or due to a non-linear load that distorts the wave shape of the current drawn from the source, the apparent power will be equal to or greater than the real power. Low power factor loads increase losses in a power distribution system and results in increased cost for electrical energy use.
- LAN
- Local Area Network. The linkage of computers and/or peripherals in a limited area, usually less than two miles, which allows users to communicate and share information.
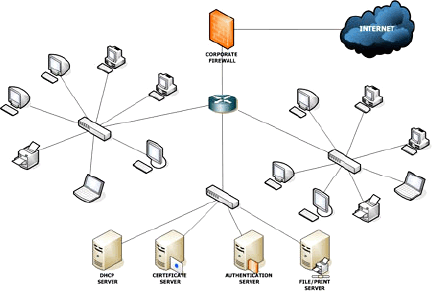 A Common LAN Schematic
A Common LAN Schematic - LCD
- Liquid Crystal Display. Refers to a flat screen display. Compared to CRT’s the big advantages include less space (e.g. smaller footprint) less power, lighter weight, greater contrast, wider screen angles. Disadvantages include lower resolution (e.g. jagged edges) higher reject rate during fabrication therefore higher costs, etc.
- Low-Voltage
- Voltages typically below 115v AC. Many data systems run on 115v AC, but telecommunications systems historically run DC to the racks at 48 volts.
- MTBF
- Mean time between failures. This is the mean (average) time between failures of a system. In other words this is the average life of a system. Hard disks specifications many times include the MTBF ratings.
- MHz
- Megahertz or one million cycles per second. This is applied to alternating currents, clock cycles in CPU’s, or even radio waves.
- N+1 or 2N
- Level of redundancy in the supporting infrastructure for a network or data center. N = need (e.g. N=2 five ton air conditioners, then N+1 = 3 five ton air conditioners; or 2N = 4 five ton air conditioners).
- NEC
- National Electric Code. (Also referred to as California Electrical Code or NFPA 70.) It is a standard for the safe installation of electrical wiring and equipment. While the NEC is not itself a U.S. law, NEC use is commonly mandated by state (including California) or local law, as well as in jurisdictions outside of the United States. The NEC codifies the requirements for safe electrical installations into a single, standardized source.
- NEMA
- National Electrical Manufacturers Association, a U.S. industry group representing those who design and manufacture electrical equipment
- NFPA
- National Fire Protection Association, is an independent, voluntary-membership, nonprofit (tax-exempt) organization. NFPA’s mission is to reduce the burden of fire and other hazards on the quality of life by providing and advocating scientifically-based consensus codes and standards, research, training, and education. NAPA publishes many standards used by local fire departments to establish minimums for fire protection systems, including Fire Sprinklers.
- NOC
- Network Operation Center. Similar to a SOC but this will monitor the entire network center on a 24/7 basis, sometimes including several distant data centers.
- Patch Panel
 This is a sophisticated name for a hub with many connections. This is where the network cables connect to the network servers from the clients or desktop computers. It is used to route the many signals into the servers or other switches.
This is a sophisticated name for a hub with many connections. This is where the network cables connect to the network servers from the clients or desktop computers. It is used to route the many signals into the servers or other switches.- Punch Down Block
 This is similar to the patch panels, but it is utilized for analog voice or telecommunications wires.
This is similar to the patch panels, but it is utilized for analog voice or telecommunications wires.- PDU
- Power Distribution Unit. Power Distribution Unit (PDU) provides power distribution, and the ability to monitor the aggregate current draw as equipment is connected to the unit. Typically these filter the electrical power to prevent surges, spikes and other anomalies from reaching the data equipment…think industrial size power strips.
- Router
- A router is a device (or in some cases software in a computer) that determines the next network point to which a data packet should be forwarded toward its destination. There are lots of variations of routers depending on where they occur in a network and how much traffic they are designed to handle.
- RF (e.g. screen room)
- Radio Frequency. As you know from your physics classes, electrical circuits produce magnetic fields around the circuit and when the frequency is in the radio wavelength spectrum it is called RF. RF interference can impede smooth data flows over data wires and wireless devices hence screening and separation can become critical.
- Server
- It can either be a program or a computer that is dedicated to a certain purpose. Often it means both at the same time, but sometimes it can be important to know, especially if you’ve just been asked to install it.
- SOC
- Systems Operation Center. Typically a “Mission Control” style room where technicians can monitor the health of a data center on a 24/7 basis.
- Soft Crash
- When electrical power is unintentionally interrupted to a system and the data systems are served by emergency power (through a UPS) which cannot be reliably provided for an extended outage, the systems operators can execute a systematic shut down to bring down the systems and prevent data loss. When reliable power is reestablished the system can then be brought back up and data services restored. Conversely a Hard Crash is an instantaneous power outage which typically interrupts data flows and results in data loss…not a good thing.
- Tier 2, Tier 3, Tier 4
- Classification of the level of reliability of a data center or network as established by the Uptime Institute. It classifies systems redundancies, number of alternate data distribution paths, etc. Tier II = roughly 99.75%, Tier III = 99.98%, Tier IV = 99.99% reliability.
- Twisted pair
 A common descriptor of telephone (and data) wire. A pair of solid copper telephone wire can handle a single call discrete call prior to arriving at a switch (which usually includes devices to multi-plex or MUX to combine calls over a single twisted pair or fiber cable. (See 25 pair/300 pair).
A common descriptor of telephone (and data) wire. A pair of solid copper telephone wire can handle a single call discrete call prior to arriving at a switch (which usually includes devices to multi-plex or MUX to combine calls over a single twisted pair or fiber cable. (See 25 pair/300 pair).- UPS
- Uninterrupted Power Supply; a back-up power supply for computer systems. This can take many forms depending on the scale of the systems. It can be as small as a shoebox-sized box with sealed batteries to support a single computer (CPU) or as large as 10'x14'x14' high diesel generator, with a Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS), battery banks and/or power conditioning units.
- VA or Volt Ampere
- A volt-ampere in electrical terms, means the amount of apparent power in an alternating current circuit equal to a current of one ampere at one volt. It is dimensionally equivalent to watts. An example might be an AC transformer rated in electrical terms by volt amperes.
- VOIP or Voice over IP
- Voice over Internet Protocol, also called VoIP, IP Telephony, Internet telephony, Broadband telephony, Broadband Phone and Voice over Broadband is the routing of voice conversations over the Internet or through any other IP-based network. Essentially your voice (an analog signal) is converted at the instrument (or phone on your desk) into a data signal made up of discreet data packets just like your email message, it is then sent over the internet to an IP address where is reconverted into an analog signal at the receiver’s phone. The instrument is an I.P. type phone and the receiver has to have an I.P. phone or have the signal converted somewhere in between. This is typically handled automatically be the phone switches involved in the transfer of the signal
- W/SF
- Watts per square foot. This is sometimes used as a benchmark for how much power can be delivered to a given area. Office spaces typically need about 10~20 WSF. Data centers range for traditionally of up to 85WFS. Newer data centers that cater to Web hosting systems can now exceed 200~400WFS!
- WAN
- Wide Area Network. A computer network in which widely dispersed computers, such as those among several buildings or across a city or state, are interconnected. WANs make use of a variety of transmission media, which can be provided on a leased or dial-up basis.
- Web Server
- A program (or sometimes referring to the actual machine) that serves up web pages upon request.
* Some material excerpted from Wikipedia.org, the free online encyclopedia that anyone can edit at http://en.wikipedia.org/



